Different Types Of Motivation In Management

What are the Different Types of Motivation In Management?
Topics Covered
Motivation is the key to finishing every work possible in our life. Without motivation, goals seem unachievable and excitement reduces over time.
How many types of motivation are there in management?
There are generally 3 different types of motivation in management.
- Positive Motivation vs. Negative Motivation
- Basic Motivation vs. Learned Motivation
- Extrinsic motivation and Intrinsic Motivation
What is motivation?

- Willingness: refers to the state of readiness for a person to act
- Intense Effort: refers to how hard a person tries
- Persistence effort: refers to the continuity of the effort
Three types of Motivation in management (explained)
3 Types of Motivation in Management
- Positive Motivation vs. Negative Motivation
- Basic Motivation vs. Learned Motivation
- Extrinsic motivation and Intrinsic Motivation
-
Positive Motivation vs. Negative Motivation
Positive vs. Negative: Motivating forces can be positive, as in impelling one to reach a certain goal. They can also be negative, as in driving one away from an undesirable situation.
You can be positively motivated about going to work because you like your colleagues and some parts of the work, and negatively motivated because you have bills to pay (moving away from poverty) and you fear that if you stop working, you cannot carry on with your lifestyle.
From the manager’s perspective, giving rewards may be a positive motivation, whereas frightening the employee with demotions, layoffs, etc. is negative motivation.
If you want to increase the amount of positive motivation in your life, or for someone else, focus on creating patterns of reward for behavior. This will reinforce the conduct you want to see. Some ideas for positive motivation are given below.
-
List everything that you will gain from your particular goal. Having a clear idea of all the positives can be very inspiring!
-
Maximize your strengths: Instead of thinking about your weaknesses, consider how you can maximize your strengths.
-
Track your progress: Dividing a larger goal into smaller milestones will help with progress. You should track these small milestones down regularly so that you may know how much you have achieved for a particular goal.
-
Give yourself a reward: reward yourself! For instance, give yourself permission to watch a movie guilt-free if you achieve a small milestone.
-
Surround yourself with encouragers. Have friends who will encourage you and want what’s best for you.
-
Basic Motivation vs. Learned Motivation
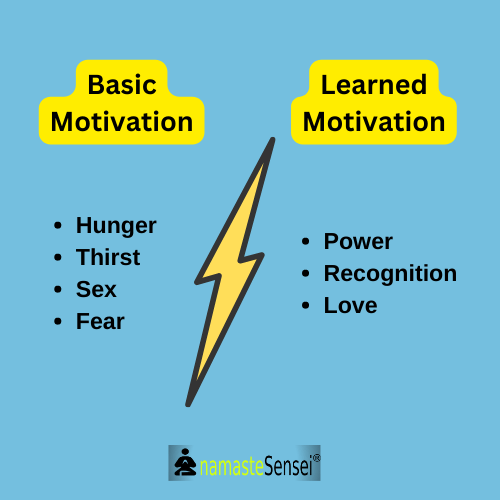
Basic vs. Learned: Motivation leans on motives. We often categorize motives into basic motives and learned motives. Basic (also known as primary) motives are unlearned and common to both animals and humans.
We’re talking about hunger, thirst, sex, avoidance of pain, and perhaps aggression and fear. The learned or secondary motives include achievement, power, recognition, and love.
-
Extrinsic motivation and Intrinsic Motivation
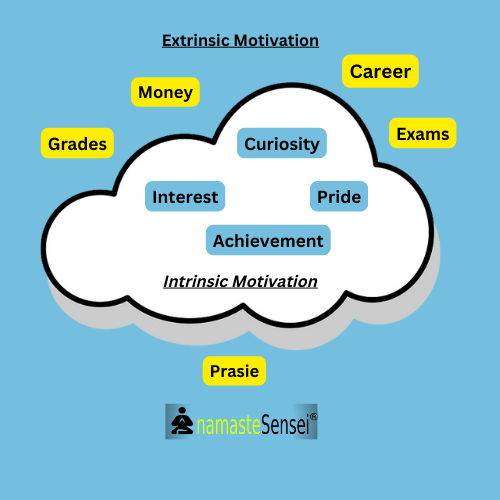
Extrinsic Motivation: Outside
Extrinsic motivation occurs when we are motivated to perform a behavior or engage in an activity to earn a reward or evade punishment. The motivation comes from outside.
Examples of behaviors that result from extrinsic motivation include:
- Studying because you want to get a good grade.
- Cleaning your room to avoid being scolded by your parents.
- Contesting in a contest to win a scholarship.
- Taking part in a sport to win awards.
Intrinsic motivation involves engaging in behavior because it is rewarding; essentially, performing an activity for its own sake rather than the desire for some external reward. It comes from inside the individual and is not done for external rewards. Intrinsically motivated people get a great deal of satisfaction and enjoyment from what they do.
Examples:
- Participating in a sport because you find the activity enjoyable.
- Solving a word puzzle because you find the challenge fun and exciting.
- Playing a game because you find it exciting.
Every team member is distinctive and will probably have different motivators. So, it’s important to get to know your people, discover what motivates them, and find a pleasant mixture of extrinsic and intrinsic motivators, so that you can encourage them successfully.
What are motivators?
A motivator is anything which satisfy your need. For example, for a Hungry person, the motivator would be availability of food.
For example, an employee wants to buy a car and is feeling frustrated without a car. For such an employee, a salary raise might be the biggest motivation. On the other hand, an employee is feeling dissatisfied because the employee is not finding the work challenging.
For such an employee, a salary rise might not be an excellent motivator, only a challenging project can motivate the employee.
Different Types of Motivation theories in management
Process-Based Theories
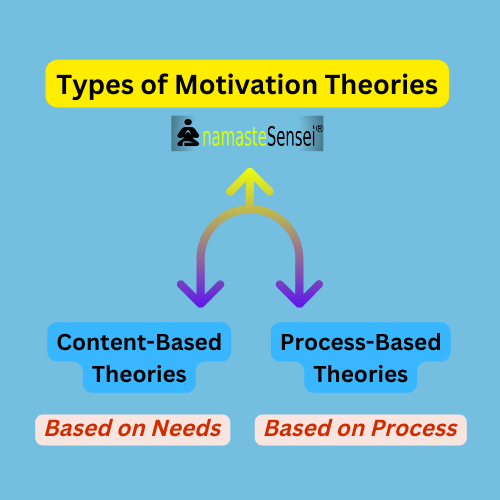
Content-Based Theories: Content Theories look at precise needs that motivate people. The need can be intrinsic or extrinsic needs and hence managers should know the needs of everyone. This basically focuses on what motivates an individual. We also know these as traditional theories. Some of the Content-Based types of motivation theories are given below.
- Maslow’s Motivation theory
- Alderfer’s Hierarchy of Motivation needs (ERG theory)
- Mcclelland’s theory of needs
- Herzberg’s Two-factor theory
- McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y
- Instinctive Theory of Motivation
Process-Based Theories: Process theories try to explain how the process of motivation works in an individual. Individuals make choices based on preferences, rewards, and achievements, and therefore managers need to understand the process of motivation. We also know these as contemporary theories. Some of the Process-Based types of motivation theories are given below.
- Self-Determination Theory by Deci and Ryan
- Adam’s Equity Theory
- Hackman and Oldham’s Job Characteristics model
- Cognitive Evaluation Theory
- Vroom’s Expectancy Theory
- Porter and Lawler’s Model of Motivation
- Argyris’s Theory of Motivation
- Self-Efficacy Theory by Albert Bandura
- Reinforcement Theory by E.L. Thorndike
- Hawthorne Effect by Henry A. Landsberger
- Edwin Locke’s Goal-Setting Theory
- Clark Hull’s Drive Reduction Theory
- Three-Dimensional Theory of Attribution by Bernard Weiner
Congratulations, you have read the complete article about different types of motivation in management.
If you have any doubts or queries, feel free to comment below. We will respond as soon as possible.
Or Email Us At [email protected]
Any topic you want us to cover? Let us know.

This is an outstanding piece of content. I’m impressed by how well you’ve explained the subject.