Clayton Alderfer’s erg theory of motivation With Examples
Clayton Alderfer’s Erg Theory of Motivation
Topics Covered
What is ERG theory Of Motivation?
Alderfer believed that the original need hierarchy was not quite accurate in identifying and categorizing human needs. So he came up with the ERG theory of motivation which is a simplified interpretation of Maslow’s theory of needs.
Hence, Alderfer proposed the ERG theory in 1969, which reduces Maslow’s five human needs: (Physiological needs, safety needs, Social needs, Self-Esteem needs, and Self-Actualization needs.) into three categories:
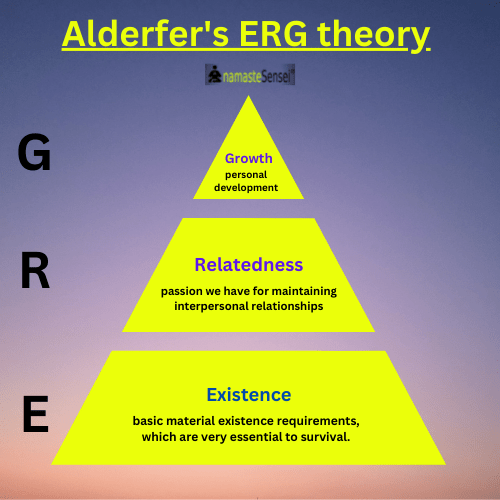
E – Existence
R – Relatedness
G – Growth.
ERG THEORY DEFINITION
- Existence refers to our concern with basic material existence requirements, which are very essential to survival. Maslow called these needs physiological and safety needs.
For Example, if a person does not have water to drink or food to eat. He will not even think about a job or education. His immediate focus will be only to satisfy his hunger or thirst. He can’t be motivated to study to make his career and find a job.
- Relatedness refers to the passion we have for maintaining interpersonal relationships (be it with family, friends, or others). In Maslow’s theory, relationships come under (social/love needs).
For Example, Employees in a company should be emotionally and physically safe. Their peers should accept them within the company so they can progress and reach their full potential. Some employees who are not accepted by their peers do not grow well.
- Growth refers to an intrinsic desire for personal development. Maslow’s esteem needs and self-actualization are simplified to growth needs in Alderfer’s theory of motivation.
For Example, Talented employees after a period come to know that they can achieve much more. An employee can realize that he has the potential to become the top sales agent in a company.To achieve this target, the employee tries his best. If his manager cannot recognize the abilities of such employees and does not respond properly to their achievements, these employees lag behind their actual level of performance.
It is the responsibility of a manager to provide interesting and varied challenges and present various growth opportunities for such employees.
difference between Maslow and eRG theory of motivation
-
Hierarchy of needs
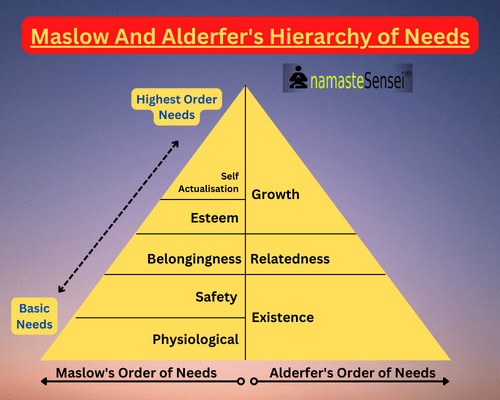
There are five needs in Maslow’s need hierarchy theory of motivation. These needs are:
- Physiological needs (lowest order need)
- Safety needs
- Social needs
- Self-Esteem needs
- Self-Actualization needs. (highest order need)
While Alderfer’s ERG Theory has only three levels of need. These were:
- Existence
- Relatedness
- Growth
-
Cause of Motivation And order of needs
In Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory, at one moment, only one level of need can cause motivation. Maslow says that physiological needs (Needs for air, water, food, defecation, etc.) are the most important and basic among all needs.
Once the lower-order needs are fulfilled, then only higher-order needs can be fulfilled.
These are the things without which we cannot live. Unless it fulfills these needs of the individual, he cannot even think of higher-level needs.
For example, If a child is starving or thirsty, the teacher cannot motivate him for learning in class.
In Alderfer’s erg theory of motivation, over one need may be operative at the same time.
This means that one might work on his Existence needs and at the same time, he might be working on his relatedness needs.
In addition to this, Alderfer also talked about the order of needs. He said that the Priority of needs will differ from person to person. Some might give priority to existence needs and others might give it to relatedness needs.
In Alderfer’s Erg Theory of motivation, there are no restrictions for following needs in a particular order, like bottom to top (in Maslow’s theory) or top to bottom.
-
Satisfaction progression vs frustrated progression
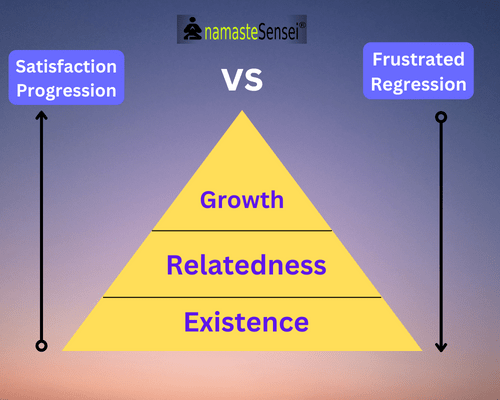
In Maslow’s theory, individuals will remain at the same level of needs until achieving satisfaction.
Satisfaction Progression: It means that only once the lower-order needs are fulfilled, then only higher-order needs can be fulfilled. This concept of lower-level needs being satisfied first before moving higher is called satisfaction progression.
For Example, a person whose physiological needs (like water, food, etc) are not fulfilled, will never ask for his safety needs such as (Financial Security, Emotional Security, etc). Physiological needs are lower-order needs that need to be fulfilled first, and safety needs are higher-order needs that need to be fulfilled later.
But in Alderfer’s ERG Theory of motivation, if needs remain unsatisfied, the individual becomes frustrated and regresses to lower-level needs.
ERG theory says that when a higher-order need level is frustrated, the individual’s desire to fulfill a lower-level need takes place.
For Example, the incapability to satisfy a need for social interaction (relatedness need) might increase the desire for more money (existence need) or better working conditions. So, frustration can lead to a regression to a lower need. This concept is called frustrated regression.
How Alderfer’s Erg theory is applied in real life?
Alderfer’s ERG theory can be used in practical contexts, including the workplace, to raise employee engagement and motivation. Several examples of how the idea might be used are given below:
- Providing for the need for existence: An organization may ensure job security by paying employees fairly and offering benefits, or by putting in place initiatives that assist staff members with financial management and budgeting.
- Addressing the desire for relatedness: An organization may encourage communication, routine team-building events, and pleasant workplace culture to foster cooperation and collaboration.
- Addressing the need for growth: Providing possibilities for career development through mentoring, training and development programs, and advancement opportunities are some ways that an organization may respond to the desire for growth.
- Addressing all three requirements at once: An organization might adopt a flat organizational structure to provide employees with more freedom, responsibility, and opportunities.
In addition, Alderfer’s ERG theory can also be applied in other settings, such as education, healthcare, and social services, to understand and address the needs of students, patients, and clients.
Importance of Alderfer’s ERG theory In the Workplace

ERG THEORY IN THE WORKPLACE
- On a work level, Alderfer’s model implies managers must recognize their employees’ multiple simultaneous needs. Hence, Focusing only on one need at a time will not motivate your people. In fact, ERG theory states that there might be more than one need that may be operative at the same time.
Managers must understand that an employee has various needs at a particular time and a manager should satisfy those needs at the same time.
Alderfer’s ERG theory of motivation states that if the manager satisfies only one need at a particular time, this will not effectively motivate the employee.
- The frustration-regression principle affects workplace motivation. For example, if growth opportunities are not provided to employees, they may regress to relatedness needs, and socialize more with co-workers. If we can recognize these conditions early, we can take steps to satisfy the frustrated needs until the employee can pursue growth again.
Content-Based Motivation Theories in management
Content-Based Theories: Content Theories look at precise needs that motivate people. The need can be intrinsic or extrinsic needs and hence managers should know the needs of everyone. This basically focuses on what motivates an individual. We also know these as traditional theories. Some of the Content-Based theories of motivation are given below.
- Maslow’s Motivation theory
- Alderfer’s Hierarchy of Motivation needs (ERG theory)
- Mcclelland’s theory of needs
- Herzberg’s Two-factor theory
- McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y
- Instinctive Theory of Motivation
Recommended Read: Types Of Motivation In Management With Examples
Alderfer’s ERG theory PDF
Congratulations, you have read the complete article about Clayton Alderfer’s Erg Theory of Motivation
If you have any doubts or queries, feel free to comment below. We will respond as soon as possible.
Or Email Us At [email protected]
Any topic you want us to cover? Let us know.

