Advertisements
Judicial Review in India
What is Judicial Review in india?
- Judicial Review in India means the power of the Supreme Court and High court to declare a law unconstitutional and void if it violates one or more provisions of the constitution.
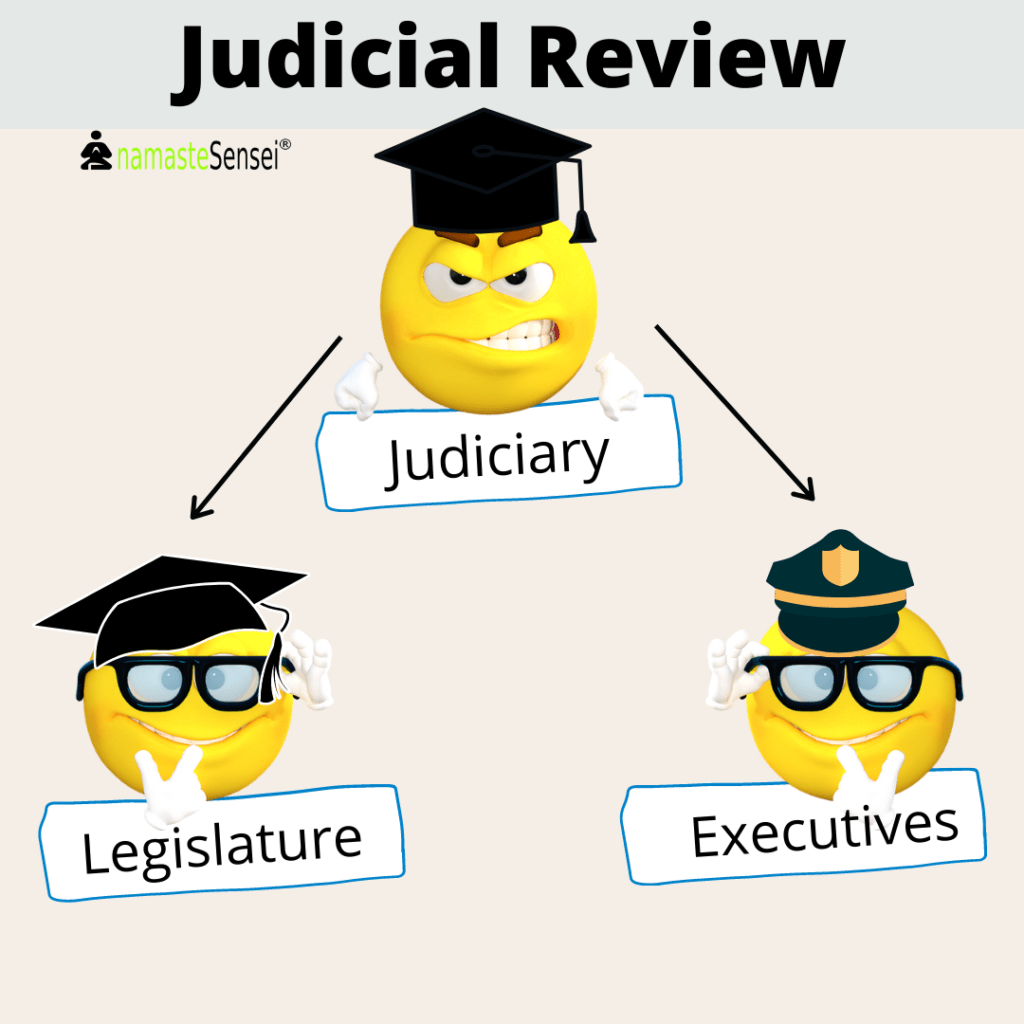
- The power of review is available with the court against the action of the legislature and Executive both.
- Judicial Review in India is not directly expressed in the Indian constitution. It is to inferred under article 32 & article 226.
Article 32- Writ jurisdiction of the supreme court.
Article 226- Writ jurisdiction of the High court.
Explanation
NOTE: The word “Judiciary Review” is nowhere mentioned explicitly in the constitution.
-
How Judicial Review is helpful?
- For Example: If any administration is doing something unwise and unconstitutional, then the state can prevent such a thing from happening.
- Similarly, if the state has done something unwise & unconstitutional then the judiciary can approve/disapprove the work of the state with the help of such review.
-
Which Article gives power to Judiciary to take Judiciary review IN INDIA?
ARTICLE 13
- Article 13 (only concerning the Fundamental Rights).
- Any other action by the administration or state will not be given power under Article 13 of the Indian constitution.
ARTICLE 32
- Article 32 gives power to the Supreme Court to restore the Fundamental Right violated by the state or administration.
ARTICLE 226
Advertisements
- Article 226 gives power to the High Court to restore the Fundamental Right violated by the state or administration.
-
Is Article 13, Article 32, Article 226 are the only provisions that ensure Judicail review?
There are other commentaries also such as
- Supremacy of the constitution.
- Concept of limited government.
- Rule of Law.
- Separation of Powers.
- Fundamental rights etc.
- The doctrine of limited government, the supremacy of the constitution, rule of law, separation of powers, Fundamental rights, etc ensures Judicial Review in India.
Application of Judicial Reveiw
- It can be applied on an act or order comes into force (not in the bill stage).
- Ordinarily, the courts apply for judicial review on basis of a petition filed and not on Suo Motu on its own.
SUO MOTU means action taken by the court on its own. - Judicial review also help the courts to act as a protector of fundamental Rights and ensures constitutionalism helps in validation of the laws passed by the state.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is judicial review is a part of the basic structure of the constitution?
- Realizing its importance in Minerva Mill Case the Supreme Court said that the power of Judicial Review is part of the basic structure of the constitution.
- What is the supremacy of the constitution?
- What is a limited government?

Advertisements
A limited government is a system in which the primary leaders have very little governing power over the decisions and laws that are created without approval from other branches or leaders within the government.
- Is there any judicial review article?
- No there is no article specifically made for it, as it is not mentioned in the constitution explicitly.
- What is the basic structure of the constitution?

- The basic structure of the constitution are those parts and features of the constitution without which the constitution loses its character.
- The Supreme Court did not define exhaustively (completely) the basic structure of the constitution but in various judgments, we keep knowing them.
Example: Judicial Review, Secularism, Sovereignty, Federalism, the mandate to build a welfare state, etc.
If you have any doubts or queries, feel free to leave a comment below. We will respond as soon as possible.
Or Email Us At [email protected]
MORE ARTICLES:
| Right to Freedom Article[19-22] | Right to Equality Article[14-18] |
| Article 14 of the Indian Constitution | Article 13 |
| Article 21 – Right to life | Article 16 of the Indian Constitution |
Any topic you want us to cover. Let us know.