Advertisements
Rule of law in Hindi
कानून का शासन

Rule of law in Hindi and English
- In India “Rule of law” concept came from England and has been made part of the Right to Equality under Article 14 of the Indian Constitution.
भारत में “कानून का शासन” की अवधारणा इंग्लैंड से आई है और इसे भारतीय संविधान के अनुच्छेद 14 के तहत समानता के अधिकार का हिस्सा बनाया गया है।
- This concept was given by A.V DICEY.
यह अवधारणा A.V DICEY द्वारा दी गई थी। - However, Laws are made for the welfare of the people to maintain harmony between the conflicting forces in society.
हालाँकि, समाज में परस्पर विरोधी ताकतों के बीच सामंजस्य बनाए रखने के लिए लोगों के कल्याण के लिए कानून बनाए जाते हैं। - One of the prime objectives of making laws is to maintain law and order in society and develop a peaceful environment for the progress of the people.
कानून बनाने का एक प्रमुख उद्देश्य समाज में कानून व्यवस्था बनाए रखना और लोगों की प्रगति के लिए शांतिपूर्ण वातावरण का विकास करना है।
What is the Rule of Law in India?
कानून का शासन क्या है?
- It means “Law Is Supreme” i.e “Lex Supremus” and absolute supremacy of the law against the arbitrary powers.
इसका अर्थ है “कानून सर्वोच्च है” यानी “लेक्स सुप्रीमस” और मनमानी शक्तियों के खिलाफ कानून की पूर्ण सर्वोच्चता।
| What are Arbitrary Powers? मनमानी शक्तियां क्या हैं? |
| Powers that are unrestricted and have no logic. For example: punishing someone without reason is against the right to equality. शक्तियाँ जो अप्रतिबंधित हैं और जिनके पास कोई तर्क नहीं है। उदाहरण के लिए: किसी को अकारण दंडित करना समानता के अधिकार के विरुद्ध है। |
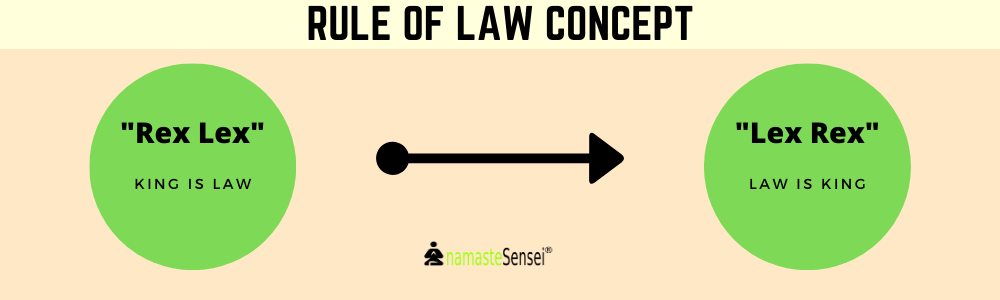
- Only the adoption of the Rule of Law has changed the concept of Rex Lex (King is Law) to Lex Rex (Law is King) which is very much essential for the right to equality & stability in India.
केवल कानून के शासन को अपनाने ने Rex Lex (King is Law) की अवधारणा को Lex Rex (Law is King) में बदल दिया है जो भारत में समानता और स्थिरता के अधिकार के लिए बहुत आवश्यक है।
Advertisements
- Explanation:
Lex- Law
Rex- King - Lex is Rex- Law is King (Now)
- Rex is Lex- King is Law (In Past)
- Constitution under Article 32 and Article 226 empowers Supreme Court and High Court to enforce the Rule of Law against executives and legislators.
अनुच्छेद 32 और अनुच्छेद 226 के तहत संविधान सर्वोच्च न्यायालय और उच्च न्यायालय को कार्यपालकों और विधायकों के खिलाफ कानून का शासन लागू करने का अधिकार देता है। - The Supreme Court also held that the Rule of Law is a part of the basic structure of the Constitution in India and also a part of the Right to equality. It cannot be destroyed even by an amendment.
सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने यह भी माना कि कानून का शासन भारत में संविधान की मूल संरचना का एक हिस्सा है और समानता के अधिकार का भी एक हिस्सा है। इसे संशोधन द्वारा भी नष्ट नहीं किया जा सकता।
Three principles of Rule of law in Hindi
कानून के शासन के तीन सिद्धांत
- No man shall be punished or made to suffer except for a violation of Law and such violation should have been established in an Ordinary court of Law.
कानून के उल्लंघन के अलावा किसी भी व्यक्ति को दंडित या पीड़ित नहीं किया जाएगा और इस तरह के उल्लंघन को एक साधारण अदालत में स्थापित किया जाना चाहिए था। - All persons are subjected to the Ordinary Law of land without any distinction i.e all can sue or get sued before the court.
सभी व्यक्ति बिना किसी भेद के भूमि के साधारण कानून के अधीन हैं अर्थात सभी अदालत में मुकदमा कर सकते हैं या मुकदमा कर सकते हैं।
Can sue or get sued– means anyone can start legal proceedings against someone and also vice-versa.
Can Sue or get sued– इसका मतलब है कि कोई भी किसी के खिलाफ कानूनी कार्यवाही शुरू कर सकता है और इसके विपरीत भी। - It says that all the laws passed by the legislature must be consistent with the provisions of the constitution.
इसमें कहा गया है कि विधायिका द्वारा पारित सभी कानून संविधान के प्रावधानों के अनुरूप होने चाहिए।
Exceptions to rule of law in Hindi
कानून के शासन के अपवाद
- The President or the Governor is not answerable to any court for the exercise of the powers and duties of his office.
राष्ट्रपति या राज्यपाल अपने कार्यालय की शक्तियों और कर्तव्यों के प्रयोग के लिए किसी भी अदालत के प्रति जवाबदेह नहीं हैं। - Members of Parliament (M.P), ministers, and other executive bodies are also given wide discretionary powers.
संसद सदस्यों (एमपी), मंत्रियों और अन्य कार्यकारी निकायों को भी व्यापक विवेकाधीन शक्तियां दी जाती हैं।
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले प्रश्न
What is the basic structure of the constitution?
संविधान की मूल संरचना क्या है?

- The Basic Structure of the constitution consists of those parts and features of the constitution without which the constitution loses its character.
संविधान की मूल संरचना में संविधान के वे भाग और विशेषताएं शामिल हैं जिनके बिना संविधान अपना चरित्र खो देता है। - The Supreme Court did not define exhaustively the basic structure of the constitution but in various judgments, we keep knowing them.
सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने संविधान की मूल संरचना को विस्तृत रूप से परिभाषित नहीं किया लेकिन विभिन्न निर्णयों में, हम उन्हें जानते रहते हैं।
Example: Judicial Review, Secularism, Sovereignty, Federalism, the mandate to build a welfare state, etc.
उदाहरण: न्यायिक समीक्षा, धर्मनिरपेक्षता, संप्रभुता, संघवाद, कल्याणकारी राज्य बनाने का जनादेश, आदि।
Example: Judicial Review, Secularism, Sovereignty, Federalism, the mandate to build a welfare state, etc.
बधाई हो, आपने पूरा लेख पढ़ा। यदि आपके कोई संदेह या प्रश्न हैं, तो बेझिझक नीचे टिप्पणी करें। हम जितनी जल्दी हो सकेगा संपर्क करेंगे।
या हमें ईमेल करें
अधिक लेख:
| Right to Freedom Article[19-22] | Right to Equality Article[14-18] |
| Article 14 of the Indian Constitution | Article 13 |
| Article 21 – Right to life | Article 16 of the Indian Constitution |
Any topic you want us to cover. Let us know.
Advertisements
